 |  | |
| A unique electrical resistivity experiment reveals the 3D interior of Piton de la Fournaise | ||
Understanding the internal structure of volcanoes is essential for improving eruption predictions and assessing hazards. Achieving high-resolution 3D models of their interiors remains challenging. At Piton de la Fournaise, we used 3D electrical resistivity tomography to generate the first high-resolution image beneath the Terminal Cone, extending to one kilometer deep. Our model reveals a large hydrothermal zone beneath layered lava flows, with conductive offshoots extending toward the surface beneath the Bory crater and along faults linked to the Dolomieu crater. These results indicate that hydrothermal activity is strongly influenced by volcano-tectonic features at the summit. This study provides valuable insights into fluid circulation, magma transfer, and instability, offering a new framework for understanding the spatio-temporal evolution of Piton de la Fournaise and other volcanoes worldwide. | 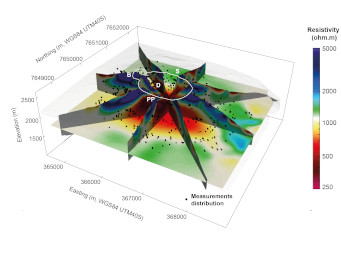 | |
| Downloads and links | ||
| Data | Fournaise_Inv_res.zip | |
| | DataCite - XML - JSON | |
| Interoperable | https://catalog.opgc.uca.fr/geonetwork2/srv/eng/catalog.search#/metadata/63914de8-e604-4356-93bd-81d0e0a36603 | |
| Links | https://lmv.uca.fr/scan4volc/ | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.25519/W9J6-TD91 DOI | |
About this resource | ||
| Keywords | Geology, Piton de la Fournaise, 3D electrical resistivity, Modeling, Hydrothermal system, Preferential fluid path, Dataset | |
Ressource Type | Dataset | |
| License | Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International | |
Funding references | ||
| Creators | Lydie-Sarah Gailler, Romain Guillard, Solène Buvat, Philippe Labazuy, Anthony Finizola, Roulleau Emilie | |
Creation date | 2024-05-05 | |
| Publisher | OPGC, LMV | |
Publication year | 2024 | |
Technical information | ||
Spatial extent | ||
| Formats | VTU, PVSM, MP4 | |
| Software | ||
| Lineage | ||